Rigid ESALs or E -18s Flexible ESALs or E-18s. Use the 1993 AASHTO Empirical Equation Using the previously calculated ESAL results and the 1993 AASHTO empirical rigid pavement design equation the following pavement thickness designs can be calculated. aashto rigid pavement design.
Aashto Rigid Pavement Design, 300 a vi 74 p. AASHTO Pavement Thickness Design Guide When designing pavement thickness for flexible and rigid pavements the following considerations should be used. Validation of Guidelines for k-Value Selection and Concrete Pavement Performance Prediction Results Project 000 Description.
 7 Rigid Pavement Thickness Design Chart Source Aashto 1993 Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
7 Rigid Pavement Thickness Design Chart Source Aashto 1993 Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
It allows compliant concrete pavement designs to be completed in minutes with our unique design analysis tools showing the designer at a glance the optimum concrete pavement thickness. 300 a vi 74 p. UFC design method - Calculate the required thickness of rigidconcrete pavement over modifiedstabilized subgrade.
300 a vi 74 p.
Performance criteria serviceability indexes. I1007248 11 Rigid Pavement Types. AASHTO DESIGN Traffic ESALs or E-18s The number and weight of all axle loads from the anticipated vehicles expected during the pavement design life - expressed in 18-kip 80 kN Equivalent Single Axle Loads for each type of pavement. The steps in the 1993 AASHTO rigid pavement design procedure are summarized below in the context of the example baseline scenario presented in Section 621. W 18 189 million ESALs. A Guide for design of pavement structures 246.
Another Article :

When a stiff layer bedrock etc is located within 10 ft 3 m of the surface the stiff layer will provide additional support for the pavement. AASHTO 1993 from publication. Download scientific diagram 7. Subgrade M R. Mechanistic-Empirical Pavement Design Guide. Structural Design Of Highway Flexible Pavement Design Highway.

Use the 1993 AASHTO Empirical Equation Using the previously calculated ESAL results and the 1993 AASHTO empirical rigid pavement design equation the following pavement thickness designs can be calculated. Based on Figure 36 in the 1993 AASHTO Guide for Design of Pavement Structures a Loss of Support 10 results in k eff 250. Mechanistic-Empirical Pavement Design Guide. Determine the analysis period. UFC design method - Calculate the maximum length of steel reinforced rigidconcrete pavement. Typical Road Structure Cross Section Sub Grade Base Course Sub Base Wearing In 2021 Civil Engineering Design Civil Engineering Construction Structure And Function.

So we must check if the final SN 3 is similar to the assumed SN. Performance criteria serviceability indexes. AASHTO Rigid Pavement Structural Design. January 2019 Table of Contents vii FIGURES Figure Title Page No. This revised manual provides an overview of the methodology termed mechanistic-empirical or M-E pavement design. 5 Design Chart For Flexible Pavements Using Mean Values For Each Input Download Scientific Diagram.

Rigid Pavement Thickness Design Chart Source. Where k is in lbin3 and MR is in lbin2. UFC design method - Calculate the maximum length of steel reinforced rigidconcrete pavement. Mechanistic-Empirical Pavement Design Guide. Evaluate the design traffic. 7 Rigid Pavement Thickness Design Chart Source Aashto 1993 Download Scientific Diagram.

Subbase thickness10 Subbase modulus30000 psi Subgrade M R10000 psi To get k. 21 ASPHALT BASE OPTION 2-2 22 SPECAIL SELECT SOIL BASE OPTION 2-3 31 FLORIDA RIGID PAVEMENT DESIGN CLIMATIC REGIONS 3-6 61 CONCRETE SHOULDER WITH ASPHALT BASE 6-4 81 MECHANISM OF PUMPING 8-4. AASHTO Pavement Thickness Design Guide When designing pavement thickness for flexible and rigid pavements the following considerations should be used. B ill maps. Mechanistic-Empirical Pavement Design Guide. Design Of Semi Rigid Type Of Flexible Pavements Sciencedirect.

B AASHTO c c1998. Development of a Structural. Download scientific diagram 7. Subbase thickness10 Subbase modulus30000 psi Subgrade M R10000 psi To get k. AASHTO Pavement Thickness Design Guide When designing pavement thickness for flexible and rigid pavements the following considerations should be used. Salukitecture Permeable Paving Units Permeable Paving Permeable Permeable Pavers.

When a stiff layer bedrock etc is located within 10 ft 3 m of the surface the stiff layer will provide additional support for the pavement. B ill maps. Subbase thickness10 Subbase modulus30000 psi Subgrade M R10000 psi To get k. Rigid Pavement Design Anchor. AASHTO Pavement Thickness Design Guide When designing pavement thickness for flexible and rigid pavements the following considerations should be used. 1993 Aashto Rigid Pavement Structural Design Pavement Interactive.
Performance criteria serviceability indexes. Validation of Guidelines for k-Value Selection and Concrete Pavement Performance Prediction Results Project 000 Description. Higher SN means stronger pavement thus the impact of traffic on pavement deteriorations is less. Where k is in lbin3 and MR is in lbin2. A Manual of Practice 3rd Edition. 2.

The CivilWeb AASHTO Rigid Pavement Design Spreadsheet completes the design of concrete roads or pavements in accordance with AASHTO 1998. Topic 10 AASHTO Rigid Pavement Design Figure 1218 312 Pavement With Subbase cont Example. A Manual of Practice 3rd Edition. I1007248 11 Rigid Pavement Types. So we must check if the final SN 3 is similar to the assumed SN. Aashto Nomo Graph For Flexible Pavement Design Download Scientific Diagram.

Performance criteria serviceability indexes. AASHTO 1993 from publication. UFC design method - Calculate the maximum length of steel reinforced rigidconcrete pavement. Topic 10 AASHTO Rigid Pavement Design Figure 1218 312 Pavement With Subbase cont Example. January 2019 Table of Contents vii FIGURES Figure Title Page No. 7 Rigid Pavement Thickness Design Chart Source Aashto 1993 Download Scientific Diagram.

Different pavement types use different types of joints and reinforcement to control the forces acting on the concrete pavement. Topic 10 AASHTO Rigid Pavement Design Figure 1218 312 Pavement With Subbase cont Example. A Guide for design of pavement structures 246. 21 ASPHALT BASE OPTION 2-2 22 SPECAIL SELECT SOIL BASE OPTION 2-3 31 FLORIDA RIGID PAVEMENT DESIGN CLIMATIC REGIONS 3-6 61 CONCRETE SHOULDER WITH ASPHALT BASE 6-4 81 MECHANISM OF PUMPING 8-4. Topic 10 AASHTO Rigid Pavement Design Figure 1218 312 Pavement With Subbase cont Example. 12 Aashto Rigid Pavement Design Method Youtube.

Topic 10 AASHTO Rigid Pavement Design Figure 1218 312 Pavement With Subbase cont Example. Subgrade M R. Subbase thickness10 Subbase modulus30000 psi Subgrade M R10000 psi To get k. UFC design method - Calculate the frost penetration depth for flexible and rigidconcrete pavement. For the example design scenario a 30-year design life is specified. 5 Design Chart For Rigid Pavement Segment 1 Source Aashto Guide 1993 Download Scientific Diagram.
So we must check if the final SN 3 is similar to the assumed SN. Topic 10 AASHTO Rigid Pavement Design Figure 1218 312 Pavement With Subbase cont Example. It allows compliant concrete pavement designs to be completed in minutes with our unique design analysis tools showing the designer at a glance the optimum concrete pavement thickness. AASHTO Pavement Thickness Design Guide When designing pavement thickness for flexible and rigid pavements the following considerations should be used. Subbase thickness10 Subbase modulus30000 psi Subgrade M R10000 psi To get k. 2.
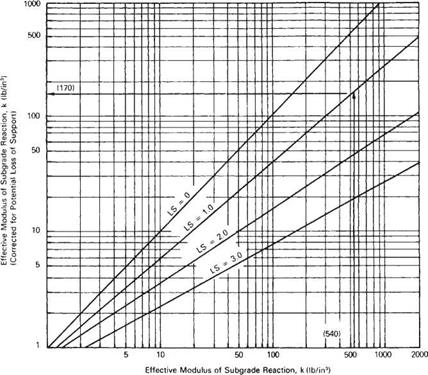
Development of a Structural. The steps in the 1993 AASHTO rigid pavement design procedure are summarized below in the context of the example baseline scenario presented in Section 621. Subbase thickness10 Subbase modulus30000 psi Subgrade M R10000 psi To get k. Where k is in lbin3 and MR is in lbin2. The design procedures main objective is to determine the thickness of the concrete slab that will be adequate to carry the projected traffic load for the design period. Rigid Pavement Design Procedure Library Builder.

Rigid Pavement Design Manual Revised. Download scientific diagram 7. Use the 1993 AASHTO Empirical Equation Using the previously calculated ESAL results and the 1993 AASHTO empirical rigid pavement design equation the following pavement thickness designs can be calculated. When a stiff layer bedrock etc is located within 10 ft 3 m of the surface the stiff layer will provide additional support for the pavement. In the AASHTO flexible pavement design traffic is considered in terms of ESAL for the terminal PSI Table 2013 for p t 25 We must assume the structural number of the pavement. Flexible Pavement Thickness Design Aashto Method Source Chapter.










